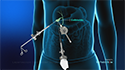
Distal Pancreatectomy
A distal pancreatectomy is a surgery performed to remove the body and tail of the pancreas. Oftentimes, the spleen, which lies close to the tail of the pancreas is also removed during this procedure, in which case the surgery is known as a distal pancreatosplenectomy.
Disease Overview
The pancreas is located in the upper portion of the abdomen behind the stomach. It functions as an organ of the digestive system and a gland as it produces digestive juices and hormones that help regulate blood sugar levels. The abnormal growth of pancreatic cells can lead to pancreatic cancer. Other types of tumors and cysts may also develop in the pancreas. Most pancreatic cancers are formed in the cells that produce digestive enzymes.
Signs and symptoms of pancreatic cancer generally occur at an advanced stage. They include yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes (jaundice), upper and middle abdominal pain, back pain, unexplained weight loss, appetite loss, fatigue, dark-colored urine, and light-colored stools.
You are at an increased risk of developing pancreatic cancer if you are a smoker, overweight, have diabetes, or have a family history of pancreatitis (inflammation of the pancreas) or pancreatic cancer.
Indications
A distal pancreatectomy may be indicated for the following conditions:
- Malignant and benign pancreatic tumors
- Pancreatic cysts or pseudocysts
- Pancreatic abscesses
- Neuroendocrine tumors
- Metastatic tumors
- Trauma
- Chronic pancreatitis
Preparation
Preoperative preparation for a distal pancreatectomy may involve the following steps:
- A thorough history and physical examination
- Routine blood work and imaging
- Informing your doctor of any medications or supplements you are taking
- Refraining from blood thinners, aspirin, or NSAIDs, if indicated
- Informing your doctor of any allergies to medications, anesthesia, or latex
- Refraining from solids or liquids at least 8 hours prior to the procedure
- Arranging for someone to drive you home after the procedure
Surgical procedure
A distal pancreatectomy procedure is a complex surgery that typically takes a few hours and can be performed laparoscopically or as an open surgery. In general, the procedure involves the following steps:
- You will lie down on the procedure table in a face-up position.
- General anesthesia is administered through an intravenous (IV) line in the arm to keep you asleep throughout the procedure.
- A surgical incision is made to enter the abdominal cavity and access your pancreas and other organs. In the laparoscopic technique, 2-3 keyhole incisions are made.
- The pancreas is divided at the neck or body depending on the location of the tumor and the distal part of the pancreas is carefully removed without damaging the blood supply to the surrounding structures. The spleen may also be removed if affected by the disease.
- Your surgeon then reconnects the cut ends of your pancreas with sutures.
- A drainage tube may be inserted to drain fluids from the operation site.
- Finally, the skin incision is sutured and a sterile dressing is applied to complete the procedure.
Postoperative care
Post-procedure care and instructions may involve the following:
- You will be transferred to the recovery area where your nurse will monitor your vital signs and watch for any signs of complications as you recover from the effects of anesthesia.
- You may need to spend at least 3-5 days in the hospital depending on your overall recovery.
- You will not be able to drink or eat normally for a few days. Your diet will be slowly advanced as tolerated, starting with a liquid diet and slowly progressing to a soft diet, and then solids within a week’s time.
- Various medications such as antacids, antibiotics, pain relievers, and anti-inflammatories are provided as needed to keep you comfortable.
- Refrain from strenuous activities or lifting weights for a specified period. A gradual increase in activities is recommended.
- You should be able to return to normal activities in about a month’s time with certain activity restrictions. Complete recovery may take 2 to 6 months.
Risks and Complications
As with any surgery, risks and complications may occur with a distal pancreatectomy, including:
- Infection
- Bleeding
- Fluid accumulation
- Leakage from the pancreatic duct
- Diarrhea
- Diabetes
- Weight loss
Summary
A distal pancreatectomy is a surgery to remove the body and tail of the pancreas. It is a surgical remedy for pancreatic tumors, chronic pancreatitis, or pancreatic injury. The surgery is quite complex and requires 3-5 days’ stay in the hospital for postsurgical recovery, but it can enhance life expectancy of patients afflicted with cancer of the pancreas or other pancreatic disorders.