Laparoscopic Hernia Repair
Laparoscopic hernia repair is a minimally invasive surgical procedure used to repair hernias. During this procedure, small incisions are made near the hernia site, and a laparoscope (a thin, flexible tube with a camera and light) is inserted to view the hernia and surrounding tissue. The surgeon then uses small instruments to push the herniated tissue back into place and reinforce the weakened abdominal wall with mesh or sutures.
Disease Overview
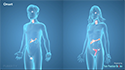
A hernia occurs when an organ or tissue protrudes through a weak spot in the surrounding muscle or connective tissue that normally holds it in place. This can result in a visible bulge or lump, often accompanied by discomfort or pain. Hernias can develop in any part of the body; however, most affect the muscles of the abdominal wall.
Some of the common types of hernia include:
- Inguinal: Part of the intestine protrudes through the lower abdominal muscle into the groin.
- Femoral: Fat tissue or part of the intestine protrudes through the abdominal muscle into the femoral artery present in the upper part of the thigh.
- Incisional: Tissue protrudes through a previous surgical wound, which becomes structurally weak.
- Umbilical: Fat tissue or part of the intestine protrudes through the abdominal muscle near the belly button.
- Hiatal: Part of the upper stomach protrudes through an opening in the diaphragm into the chest region
Indications
Laparoscopic hernia repair is indicated for various types of hernias, depending on their size, location, and the patient's overall health. It is usually recommended to treat hernias that are smaller in size and less complex. Patients with recurring hernias, bilateral inguinal hernias, and femoral hernias are especially considered as good candidates for laparoscopic hernia repair.
Preparation
In general, preparation for laparoscopic hernia repair may involve the following:
- A thorough medical evaluation by your healthcare provider to assess your overall health, including any pre-existing conditions, medications or supplements you are taking, and any allergies you may have.
- Your surgeon may instruct you to avoid certain medications and supplements that can thin the blood and increase the risk of bleeding during surgery.
- You should not consume solids or liquids at least 8 hours prior to surgery.
- You should arrange for someone to drive you home after the surgery.
- A signed informed consent form will be obtained from you prior to surgery.
Surgical procedure
In general, a laparoscopic hernia repair is usually performed under general anesthesia and may involve the following steps:
- Your surgeon makes several small incisions near the hernia site. These incisions are typically made in the abdomen, around the hernia location.
- The abdomen is inflated with a harmless gas (carbon dioxide) to help your surgeon view the treatment area more clearly, and to create ample space for the surgeon to work.
- A laparoscope, which is a thin, flexible tube with a camera and light source, is inserted through one of the incisions. The camera allows the surgeon to view the internal structures of the abdomen on a monitor.
- Specialized surgical instruments are inserted through the other incisions. These instruments are used to perform the hernia repair.
- If necessary, the hernia sac or protruding tissue (such as intestine or abdominal contents) is gently pushed back into its normal position within the abdominal cavity.
- To strengthen the weakened area of the abdominal wall and prevent hernia recurrence, the surgeon may use a synthetic mesh or sutures to reinforce the tissue.
- Once the repair is completed, the instruments are removed, and the incisions are closed with sutures or surgical tape.
Postoperative care
After the surgery, you will be monitored in the recovery area until the effects of the anesthesia wear off. You may experience some soreness or discomfort at the incision sites. Most patients can go home the same day or the day after surgery. Your surgeon will provide instructions for postoperative care, including wound care, activity restrictions, diet, medications, and follow-up appointments. It is important to follow these instructions to ensure proper healing and recovery.
Risks and Complications
Risks and complications associated with laparoscopic hernia repair include:
- Bleeding
- Infection
- Blood clots or deep vein thrombosis (DVT)
- Recurrence of the hernia
- Chronic pain
- Anesthesia-related risks
- Injury to adjacent structures
Benefits
Laparoscopic hernia repair offers several advantages over traditional open surgery, including:
- Smaller incisions
- Less postoperative pain
- Less scarring
- Faster recovery
- Shorter hospital stay
- Reduced risk of complications such as infection and hernia recurrence
Summary
A hernia occurs when the internal organs of the abdominal cavity push through a weakened spot in the abdominal wall to form a bulge. Laparoscopic hernia repair is a minimally invasive procedure used to treat many types of hernias and takes an hour or less to complete. Patients typically experience less pain and a quicker return to normal activities compared to open surgery.