Vasectomy
Introduction
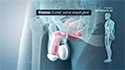
Vasectomy, also referred to as male sterilization, is a permanent method of birth control in men. It is a minor surgical procedure in which the vas deferens, the thin tube that stores and transports sperm, are cut and sealed so that the sperm can no longer enter into the urethra and cause fertilization in a woman when a man ejaculates during sexual intercourse.
Key Features of a Vasectomy
Some of the key features of a vasectomy procedure include:
- Nearly 100 percent effective in preventing pregnancy
- Low risk of complications or side effects
- Less expensive than the cost of female sterilization or tubal ligation
- No need to take birth control steps before sex, such as putting on a condom
- Very economical when compared to the long-term cost of birth control medications for women
- The safest and most effective birth control choice for men who do not wish to have children
&npsp;
Preparation for Vasectomy
Pre-procedure preparation for vasectomy may involve the following steps:
- You will be asked if you have allergies to medications, anesthesia, or latex.
- You should inform your doctor of any medications or supplements that you are taking or any medical conditions that you have that may complicate the procedure.
- Your doctor may ask you to refrain from certain blood-thinning or anti-inflammatory drugs for a defined period.
- You will be asked to take a shower on the day of surgery and wash your genital area thoroughly with an antibacterial soap.
- You will also be asked to shave the area around the penis and scrotum entirely.
- Arrange for someone to drive you home to avoid pressure or movement on the operated area caused by driving yourself.
- A signed informed consent form will be obtained from you after the pros and cons of the procedure have been explained.
&npsp;
Procedure for a Vasectomy
A vasectomy is usually performed under local anesthesia and takes about 30 minutes. In general, the procedure may involve the following steps:
- You will lie down on the procedure table in a supine position on your back.
- The surgical area in the scrotum is numbed by injecting a local anesthetic with a small needle.
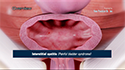
- A small incision is made on the upper part of the scrotum once the surgical area is numb. If your urologist uses another method called the "no-scalpel" technique, then a tiny puncture is made on the scrotum instead of an incision.
- Your urologist then locates the tube that carries semen from your testicle called the vas deferens and pulls out a section of it through the puncture or incision.
- The section of the vas deferens that is pulled out from the scrotum is cut and sealed by tying it, using surgical clips or a heat probe or a combination of both methods.
- Your urologist will then reinsert the ends of the vas deferens back into the scrotum.
- Finally, the surgical cut on the scrotum is closed with dissolvable stitches or glue. In some instances, your physician may leave the wound to heal on its own naturally.
&npsp;
Postoperative Care and Recovery
As a vasectomy is a same-day surgery, you will be discharged home after a few hours of observation in the recovery room with the following instructions:
- You may notice bruising, swelling and pain in the operated area for a few days. Pain relievers and anti-inflammatories are provided to address this.
- Application of icepacks on the operated area is also recommended to reduce discomfort.
- You should avoid lifting any heavy objects for a week.
- You should wear a jockstrap to support the scrotum.
- You should avoid sexual activity for one week.
- You are advised to get plenty of rest for at least a day or two.
- You should recover fully within a week; however, you may return to work in a couple of days if it is a desk job.
&npsp;
Risks and Complications of Vasectomy
Some of the risks and complications of a vasectomy may include:
- Infection at the incision site
- Bleeding within the scrotum
- Swelling, bruising, and pain around the scrotum
- Blood in the semen
- Hydrocele or fluid build-up in the testicle
- Spermatocele or a fluid-filled sac that develops close to a testicle
&npsp;
Summary
A vasectomy is a simple outpatient surgery and is considered a permanent form of male birth control. It is a safe procedure that does not affect the penis, testicles, or other internal organs. You can continue to have normal orgasms, ejaculation, erections, and a healthy sex life. A vasectomy only means that your semen or ejaculate will no longer contain sperm so you cannot make a woman pregnant.