Carotid Endarterectomy
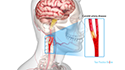
A carotid endarterectomy is a surgical procedure performed to treat carotid artery disease or CAD. It involves removal of plaque or fat deposits that accumulate within the inner lining of the carotid artery, a major vessel that supplies oxygenated blood to the brain.
Carotid artery disease is characterized by a narrowing of the lumen-or the space inside- either one or both of the carotid arteries. This restricts blood flow to the brain and could lead to either a transient ischemic attack (TIA) or a stroke. Common risk factors for carotid artery disease include:
- Age-related loss of elasticity and smoothness of the arterial walls
- High blood pressure
- Diabetes
- A high-fat diet
- Smoking
Indications
A carotid endarterectomy may be indicated for:
- Symptoms of a stroke or a transient ischemic attack which include drooping of one side of the face, weakness or numbness in one arm, and slurring of speech. These symptoms occur abruptly and may also disappear quickly. The symptoms need to be investigated as soon as possible and the procedure should be performed within 2 weeks of onset of symptoms.
- Moderate to severe carotid artery stenosis, where a 50% -99% blockage of a carotid artery is noted on diagnostic studies.
Contraindications
A carotid endarterectomy is contraindicated for:
- Mild carotid artery stenosis where less than 50% blockage of the artery is noted. This condition may be better controlled with medications and lifestyle changes.
- A complete blockage in the carotid artery. Surgical intervention is considered too risky if a 100% blockage is noted.
Preparing for Carotid Endarterectomy
Specific instructions will be provided by your surgeon. In general, you should:
- Inform your surgeon regarding any health conditions, allergies, and medications. Some of your medications may need to be stopped temporarily before surgery.
- Quit smoking as it can slow down the healing process.
- Stop eating at midnight on the day before surgery. You may have sips of water until 2 hours before the procedure.
Carotid Endarterectomy Procedure
A carotid endarterectomy procedure involves the following steps:
- Intravenous lines will be placed to administer antibiotics to prevent infection.
- You will lie on your back with your head turned away from the surgical site.
- The surgery may be performed under general or local anesthesia with the anesthesiologist monitoring your vital signs during the procedure.
- The skin over the surgical site will be cleaned with an antiseptic solution.
- An incision is made in the side of the neck to expose the carotid artery.
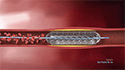
- The artery is then incised, and a shunt is used to keep blood flowing to the brain.
- Special instruments are used to remove the plaque buildup inside the artery.
- The shunt is then removed, and the incision made in the artery is closed with a special patch or sutures.
- The neck incision is closed with sutures and a bandage is placed over the surgical site.
- The surgery is completed in about 2 hours.
Recovery after a Carotid Endarterectomy
You will be moved to a recovery room and your vital signs monitored. There may be some neck discomfort for which pain medications will be provided. You will be given solid food about 2-3 hours after the surgery and discharged after 1-2 days. Your doctor will give you specific instructions regarding keeping the incision site clean and dry. You will need to have someone drive you home after the surgery. The surgical stitches may need to be removed at a follow-up appointment. Most patients can return to work or routine activities in 3-4 weeks’ time.
Risks and Complications
The risks and complications associated with a carotid endarterectomy include:
- High blood pressure
- Damage to surrounding nerves causing numbness or altered sensation
- Heart attack
- Stroke
Summary
Carotid endarterectomy is the surgical removal of plaque that builds up inside the carotid arteries due to carotid artery disease. The surgery can help reduce the risk of stroke and improves the supply of oxygen and nutrient-rich blood to your brain.