Photorefractive Keratectomy (PRK)
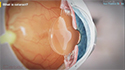
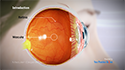
Photorefractive keratectomy, or PRK is a laser surgery performed to correct vision problems caused by refractive errors. Refractive errors occur when the eyes do not refract or bend light to properly focus on the retina, resulting in blurred vision. PRK works by reshaping the cornea using a laser, so that light entering the eye is correctly focused on the retina to deliver clear vision without the need for contact lenses or glasses.
Indications
Refractive errors for which PRK surgery is indicated include:
- Hyperopia or farsightedness
- Myopia or nearsightedness
- Astigmatism, irregular curvature of the cornea resulting in blurred vision
PRK may be recommended even if you have dry eyes or a thin cornea, which can result in complications following LASIK, a more common refractive surgery.
Who is a Good Candidate for PRK Surgery?
Some of the criteria to qualify for PRK surgery includes the following:
- Your refractive error should be one that can be corrected with PRK.
- You must be at least 18 years or older.
- Your eye prescription should not have changed in the past year.
- You should have healthy corneas.
- You should have good overall eye health.
- You should have realistic expectations about the results of the procedure.
Who is Not a Good Candidate for PRK Surgery?
You are not a good candidate for PRK surgery if you have the following issues:
- Advanced glaucoma
- Corneal disease or abrasions
- Disease or condition that can interfere with healing
- History of excessive scarring
- Changing refractive error
- History of certain eye infections
- Cataract
- Uncontrolled diabetes
- Pregnant or nursing
Preparation for Surgery
Prior to your PRK surgery, your doctor will review your medical history and perform a thorough eye examination to:
- Test your vision
- Measure your pupil size
- Measure and map the surface of the cornea
- Measure the refractive error in each eye
- Check for other eye problems
Your doctor may also give you the following preoperative instructions:
- Eat a light meal before coming for the procedure
- Take all your usual prescribed medications
- Do not apply any eye makeup
- Do not wear any bulky hair accessories
- Wear comfortable clothing
Surgical Procedure
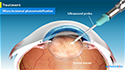
PRK is a painless procedure that is performed under local anesthesia in an outpatient setting and usually takes about 15 minutes. It involves the following steps:
- Your surgeon will first numb your eye with anesthetic eye drops.
- An eyelid holder will be placed on your eye to prevent the eye from blinking.
- You will be asked to focus on a target light so that the eye remains still.
- The outer layer of epithelial cells from the cornea is removed using a blade, special brush, alcohol solution, or laser.
- Computer-controlled pulses of light energy or laser is used to reshape the cornea.
- A contact lens is placed on the eye as a bandage for 4 to 6 days while the epithelium of the cornea heals.
- A medical professional will remove the “bandage” contact lens once the epithelium heals in 4 to 6 days.
Postoperative Care and Recovery
Postoperative care and recovery following PRK includes the following:
- Arrange for someone to drive you home.
- Keep both eyes closed and rest as much as possible during recovery.
- You may experience sensitivity to light, blurred vision, or tearing.
- Limit reading and watching TV for the first few days.
- Do not swim or use a hot tub, spa, or whirlpool for at least 2 weeks to reduce the risk of infection.
- Do not apply eye makeup, cologne, lotions, or aftershave for one week.
- Avoid strenuous activity for a week to promote healing.
- You may notice some eye pain for the first 3 days which may be controlled by medication.
- Prescription and over-the-counter eye drops are prescribed to prevent infection and keep the eyes moist.
- Wear sunglasses while outdoors to prevent discomfort from sun exposure.
- Most people can return to work in a week.
- A follow-up appointment will be scheduled to monitor your progress.
Risks and Complications
Some of the risks and complications associated with PRK surgery include:
- Scarring of the cornea
- Halos and glare around lights
- Corneal haze or cloudiness
- Infection of the cornea
- Mild corneal irregularity
- Delayed surface healing
- Worsened vision
Summary
The main objective of PRK surgery is to correct refractive errors to improve your vision. About 90 percent of individuals who have undergone PRK have attained a 20/40 vision or better without contact lenses or glasses, making it a highly successful remedy for individuals with poor vision due to refractive errors.