Total Hip Replacement
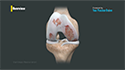
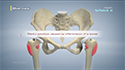
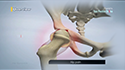
The hip joint is one of the body's largest weight-bearing joints, located between the thigh bone (femur) and the pelvis (acetabulum). It is a ball and socket joint in which the head of the femur is the ball and the pelvic acetabulum forms the socket. The joint surface is covered by a smooth articular cartilage which acts as a cushion and enables smooth movements of the joint.
A number of diseases and conditions can cause damage to the articular cartilage. Total hip replacement is a surgical procedure in which the damaged cartilage and bone is removed from the hip joint and replaced with artificial components.
Total hip replacement surgery is an option to relieve severe arthritis pain that limits your daily activities.
Arthritis is inflammation of the joints resulting in pain, swelling, stiffness and limited movement. Hip arthritis is a common cause of chronic hip pain and disability. The three most common types of arthritis that affect the hip are:
Osteoarthritis: It is characterized by progressive wearing away of the cartilage of the joint. As the protective cartilage wears down, the bone ends rub against each other and cause pain in the hip. Rheumatoid arthritis: This is an autoimmune disease in which the tissue lining the joint (synovium) becomes inflamed, resulting in the production of excessive joint fluid (synovial fluid). This leads to loss of cartilage causing pain and stiffness.
Traumatic arthritis: This is a type of arthritis resulting from a hip injury or fracture. Such injuries can damage the cartilage and cause hip pain and stiffness over a period of time.
Symptoms.
The most common symptom of hip arthritis is joint pain and stiffness resulting in limited range of motion. Vigorous activity can increase the pain and stiffness which may cause limping while walking.
Diagnosis
Diagnosis is made by evaluating medical history, physical examination and X-rays.
Surgical Procedure.
Surgery may be recommended, if conservative treatment options such as anti-inflammatory medications and physical therapy do not relieve the symptoms.
The surgery is performed under general anesthesia. During the procedure, a surgical cut is made over the hip to expose the hip joint and the femur is dislocated from the acetabulum. The surface of the socket is cleaned and the damaged or arthritic bone is removed using a reamer. The acetabular component is inserted into the socket using screws or occasionally bone cement. A liner made of plastic, ceramic or metal is placed inside the acetabular component. The femur or thigh bone is then prepared by removing the arthritic bone using special instruments, to exactly fit the new metal femoral component. The femoral component is then inserted to the femur either by a press fit or using bone cement. Then the femoral head component made of metal or ceramic is placed on the femoral stem. All the new parts are secured in place using special cement. The muscles and tendons around the new joint are repaired and the incision is closed.
Post-operative care.
After undergoing total hip replacement, you must take special care to prevent the new joint from dislocating and to ensure proper healing. Some of the common precautions to be taken include:
Avoid combined movement of bending your hip and turning your foot inwards
Keep a pillow between your legs while sleeping for 6 weeks
Never cross your legs and bend your hips past a right angle (90 degrees)
Avoid sitting on low chairs
Avoid bending down to pick up things, instead a grabber can be used to do so
Use an elevated toilet seat
Risks.
As with any major surgical procedure, there are certain potential risks and complications involved with total hip replacement surgery. The possible complications after total hip replacement include:
Infection
Dislocation
Fracture of the femur or pelvis
Injury to nerves or blood vessels
Formation of blood clots in the leg veins
Leg length inequality
Hip prosthesis may wear out
Failure to relieve pain
Scar formation
Pressure sores
Total hip replacement is one of the most successful orthopedic procedures performed for patients with hip arthritis. This procedure can relieve pain, restore function, improve your movements at work and play, and provide you with a better quality of life.